Ever wondered how electrical engineers make sense of the complex world of alternating current (AC) circuits? It's like trying to navigate a bustling city without a map. That's where phasor diagrams come in, offering a visual compass for understanding the relationship between voltage and current, especially in purely inductive circuits. These diagrams aren't just theoretical doodles; they're essential tools for designing and analyzing everything from simple inductors to complex power systems.
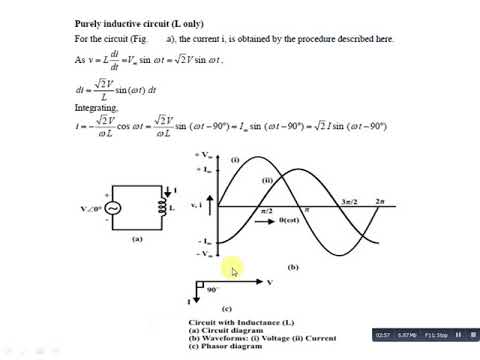
Imagine a purely inductive circuit – just an inductor connected to an AC source. Without a phasor diagram, grasping the voltage-current interplay is tricky. The current and voltage are constantly changing, making it difficult to pinpoint their relationship at any given moment. A phasor diagram simplifies this by representing these sinusoidal quantities as rotating vectors, or "phasors," allowing us to visualize their phase difference.
The fundamental principle behind a phasor diagram in a purely inductive circuit is the 90-degree phase shift between voltage and current. The voltage across the inductor leads the current by 90 degrees. This means the voltage phasor is 90 degrees ahead of the current phasor in the counter-clockwise direction, a key characteristic visualized by the diagram.
Historically, phasor diagrams emerged as a powerful tool for analyzing AC circuits, thanks to the work of pioneers like Charles Proteus Steinmetz. Before phasor diagrams, complex number calculations were the primary method for AC circuit analysis, a process significantly more cumbersome. Phasor diagrams simplified this analysis, making it more intuitive and accessible.
Understanding phasor diagrams is crucial for various electrical engineering applications. They are essential for designing efficient inductors, transformers, and other inductive components used in power systems, electronics, and communication technologies. Misinterpreting a phasor diagram can lead to design flaws, inefficient power transfer, and even system failures.
A phasor diagram for a purely inductive circuit visually represents the 90-degree phase difference. The voltage phasor points vertically upwards, while the current phasor points horizontally to the right, signifying the voltage leading the current. The length of each phasor represents the magnitude of the respective quantity.
Benefits of using phasor diagrams include simplified AC circuit analysis, clear visualization of phase relationships, and easier calculation of circuit parameters like impedance and reactance. For example, in a purely inductive circuit, the phasor diagram immediately reveals the 90-degree phase shift, allowing for quick determination of the inductive reactance.
To create a phasor diagram: (1) Draw the current phasor horizontally. (2) Draw the voltage phasor 90 degrees counter-clockwise from the current phasor. (3) Label the phasors with their respective magnitudes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplified AC circuit analysis | Only applicable to sinusoidal waveforms |
| Clear visualization of phase relationships | Can become complex for very large circuits |
| Easier calculation of circuit parameters | Doesn't provide information about transient behavior |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? (A rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.)
2. Why does voltage lead current in an inductive circuit? (Due to the inductor's opposition to changes in current.)
3. What is inductive reactance? (Opposition to AC current flow in an inductor.)
4. How is inductive reactance calculated? (XL = 2πfL, where f is frequency and L is inductance.)
5. What is the significance of the 90-degree phase shift? (It indicates energy storage and release in the inductor's magnetic field.)
6. How do phasor diagrams simplify circuit analysis? (They provide a visual representation of phase relationships, making calculations easier.)
7. What are the limitations of phasor diagrams? (They are primarily applicable to steady-state sinusoidal AC circuits.)
8. Where can I learn more about phasor diagrams? (Textbooks on circuit analysis and online resources.)
In conclusion, phasor diagrams are invaluable tools for understanding and analyzing purely inductive circuits. They provide a clear visual representation of the crucial 90-degree phase difference between voltage and current, simplifying complex AC circuit calculations. Mastering phasor diagrams empowers engineers to design and analyze inductive components and systems effectively, paving the way for advancements in various electrical technologies. By understanding these fundamental concepts, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the elegant interplay of voltage and current in the world of AC circuits. So, grab your compass – your phasor diagram – and start exploring the fascinating landscape of inductive circuits!
Unmasking the burger king foot lettuce meme mystery
Unlocking the secrets of farrow and ball showrooms
Need for speed heat installation your guide to palm city
What is a Purely Inductive Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram - Khao Tick On
Phasor Diagram For Inductive Circuit - Khao Tick On
Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - Khao Tick On
What is a Pure Inductive Circuit - Khao Tick On
SOLVED Design the circuit and sketch the waveform and the phasor - Khao Tick On
Phasor Diagram Of Pure Inductive Circuit - Khao Tick On
Phasor Diagram Of Purely Inductive Circuit - Khao Tick On
Phasor Diagram Of Capacitor - Khao Tick On
Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - Khao Tick On
What is a Pure Inductive Circuit - Khao Tick On
Inductive Circuit Phasor Diagram - Khao Tick On
What is a Purely Inductive Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram - Khao Tick On
Phasor Diagram For Inductive Circuit - Khao Tick On
Purely Resistive Purely Inductive and Purely Capacitive Circuits for JEE - Khao Tick On
phasor diagram of purely inductive circuit - Khao Tick On